Mucosal Melanoma: Insights and Treatment Options


Intro
Mucosal melanoma is a rare and serious form of melanoma that affects mucosal tissues, such as those found in the mouth, nasal cavity, and genital region. While melanoma is a well-known term, its mucosal counterpart receives significantly less attention. This lack of awareness makes understanding mucosal melanoma crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients. The interactions between genetic factors, clinical presentations, and patient experiences form the basis of this article.
Melanoma in general is recognized for its aggressive nature, and mucosal melanoma is no exception. Early detection and comprehensive treatment are essential, but the unique characteristics and the often-late diagnosis complicate management strategies.
In this article, we will explore several key aspects of mucosal melanoma, including its diagnostic challenges, treatment options, and the psychological effects on patients and their families. With this overview, we aim to equip readers with a thorough understanding of mucosal melanoma, and by doing so, improve awareness, facilitate better healthcare outcomes, and foster a compassionate environment for those affected by the disease.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Mucosal melanoma demonstrates distinct biological behavior different from cutaneous melanoma. Research indicates that mucosal melanoma commonly presents with mutations in genes such as KIT and BRAF. These mutations have implications for treatment. Additionally, the prognosis is often poorer than that of cutaneous melanoma due to late-stage diagnosis, often because of the absence of visible symptoms.
"Mucosal melanoma may account for up to 1.5% of all melanoma cases, yet it brings unique challenges in diagnosis and management."
Importance of the Research
Studying mucosal melanoma is critical not just for developing targeted treatments, but for raising awareness among medical practitioners. Improved knowledge can lead to earlier diagnosis, more effective therapeutic approaches, and better patient outcomes. Furthermore, addressing the emotional and psychological impacts of this condition is vital, highlighting the broader implications for patient care.
Methodology
Study Design
Most research on mucosal melanoma utilizes a retrospective design, analyzing patient records to assess survival outcomes and response to treatments. This approach helps identify potential patterns in clinical presentation and genetic profiles.
Data Collection Techniques
Data is usually gathered from numerous sources such as hospital databases and patient registries. This data includes information on demographics, clinical features, treatments received, and outcomes. Interviews with patients may also provide valuable insights into their experiences, reinforcing the importance of patient narratives in understanding the psychosocial aspects of the disease.
By presenting these findings, we aim to shed light on the complexities of mucosal melanoma, encouraging further investigation into this challenging condition.
Preamble to Melanoma Mucosa
Melanoma mucosa represents a lesser-known but significant aspect of melanoma. This topic deserves attention due to the unique challenges and complexities associated with this type of cancer. Mucosal melanoma mandates an understanding that goes beyond typical skin melanoma, often resulting in different clinical presentations and outcomes. Medical practitioners and researchers alike must grasp the crucial role of mucosal locations in the progression of this malignancy.
Definition and Overview
Melanoma mucosa, often termed as mucosal melanoma, refers to malignant tumors arising from melanocytes located in mucous membranes. These membranes include those found in the nasal cavity, oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and genitourinary tract. Unlike cutaneous melanoma, which mainly affects the skin, mucosal melanoma is rarer and often presents distinct histological features.
Diagnosis can be problematic due to its atypical presentation and location. Patients commonly experience symptoms that are vague or similar to other conditions. As such, early and accurate diagnosis is critical in managing this disease effectively. The rarity of this melanoma type contributes to limited data, which highlights the importance of focused research to better understand its pathology and treatment options.
This segment of the article lays the groundwork for a comprehensive examination of mucosal melanoma, addressing its distinct characteristics, diagnosis complexities, and ongoing research efforts.
Prevalence and Incidence
Mucosal melanoma is rare, accounting for only approximately 1% of all melanoma cases. Notably, the incidence is considered to be increasing in recent years. Mucosal melanoma can occur in various locations, with different rates depending on the site. For instance, oral and nasal regions have shown a slightly higher incidence compared to other mucosal sites.
Research indicates that specific demographics may be affected more frequently, including individuals over 50 years of age. However, mucosal melanoma can occur at any age. A significant concern is the fact that patients with mucosal melanoma often present at later stages, leading to a poorer prognosis when compared to those with cutaneous melanoma.
Understanding the prevalence and incidence of this condition is crucial in awareness and research initiatives, thereby influencing clinical practices and treatment strategies.
Characteristics of Melanoma Mucosa
Melanoma mucosa represents a unique and intricate variant of melanoma that demands careful study and understanding. The characteristics of melanoma mucosa play a pivotal role in distinguishing it from other forms of melanoma. This section explores histological features, morphological variations, and common sites of occurrence, providing insight into the complexity of this aggressive disease.
Histological Features
Histologically, melanoma mucosa exhibits distinct features that differentiate it from cutaneous melanoma. Under microscopic examination, the tumor often demonstrates atypical melanocytes which vary in size and shape. These atypical cells can infiltrate the epithelium and underlying connective tissues. The presence of mitotic figures is common, indicating high proliferation activity.
This type of melanoma can also show a lack of typical pigmentation, making diagnosis more challenging. A prominent feature is the associated lymphocytic response, which may suggest an immune reaction against the tumor. Understanding these histological characteristics is crucial for pathologists when diagnosing melanoma mucosa, ensuring accurate identification and appropriate treatment pathways.
Morphological Variations
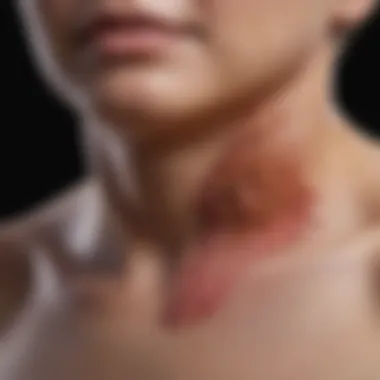

Morphological variations of melanoma mucosa can significantly influence clinical outcomes. Different growth patterns can be observed, including lentiginous, nodular, and superficial spreading types. These variations may arise from the specific mucosal site where the melanoma develops. For instance, the oral cavity may showcase different morphologies compared to the nasal cavity or anorectal region.
Identifying these variations helps clinicians tailor treatment approaches to the individual case. Some morphological types may respond better to systemic therapies or immunotherapies, while others may require surgical intervention. Understanding these variations is not just academic; it has real implications for prognosis and patient management.
Common Sites of Occurrence
Melanoma mucosa typically arises in non-sun-exposed areas, which highlights its unique etiology. Common sites of occurrence include:
- Oral cavity: often presenting as a dark lesion on the gums or palate.
- Nasal cavity: can manifest as a mass obstructing nasal airflow.
- Anorectal area: may lead to symptoms such as bleeding or change in bowel habits.
- Vulvar and vaginal regions: often misdiagnosed due to resemblance to benign lesions.
Each of these sites presents unique challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Early detection is critical, as these melanomas often go unnoticed until they reach advanced stages. Moreover, understanding the common sites helps in educating healthcare professionals and patients about the signs and symptoms that warrant medical attention.
Key Point: Recognizing the distinct characteristics of melanoma mucosa aids in timely diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Diagnosis of Melanoma Mucosa
Diagnosing melanoma mucosa presents critical challenges, given its rare nature and often late-stage presentation. Early and accurate diagnosis is paramount for improving patient outcomes and tailoring effective treatment strategies. Understanding the multifaceted elements that contribute to a proper diagnosis can guide medical professionals in recognizing and managing this aggressive form of skin cancer.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
Clinical symptoms of mucosal melanoma may be subtle, which can lead to delayed diagnosis. Patients often present with non-specific changes in mucosal areas, such as the mouth, nasal cavity, and gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms may include:
- Unusual pigmentation: Dark lesions may appear on the mucosal surfaces, often mistaken for other benign conditions.
- Pain or soreness: Patients may experience discomfort or persistent pain in the affected area, which may mislead the initial diagnosis.
- Bleeding or ulceration: These symptoms can also occur, complicating the clinical picture and potentially suggesting other conditions.
By recognizing these symptoms early, healthcare providers can prompt further investigation.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a vital role in the diagnosis of mucosal melanoma. Common methods include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Often utilized for deeper evaluation of soft tissues and the extent of lesions.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans: Useful for assessing the size and spread of melanoma in various body parts.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography): Provides functional imaging, revealing active cancer cells throughout the body.
These techniques help in staging the disease and assessing metastatic spread, which is crucial for determining treatment effectiveness.
Role of Biopsy
Biopsy is central to confirming a diagnosis of melanoma mucosa. The procedure involves obtaining a tissue sample for histopathological examination. The types of biopsies include:
- Incisional biopsy: A portion of the lesion is removed for analysis. This type may be preferred when the lesion is large.
- Excisional biopsy: The entire lesion is removed, providing a comprehensive sample for evaluation.
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA): Often used for lymph node assessment when metastasis is suspected.
A biopsy provides definitive evidence of melanoma and is essential for formulating an effective treatment plan.
Differential Diagnosis Challenges
The differential diagnosis of mucosal melanoma can be tricky due to its similarity to other conditions. Common misdiagnoses may include:
- Benign neoplasms: Such as melanocytic nevi that can resemble melanoma.
- Inflammatory conditions: Such as infections or lichen planus that can mimic the appearance of melanoma.
- Other malignancies: Various types of cancers can present in similar locations and with similar symptoms.
Healthcare providers must maintain a high index of suspicion and consider melanoma mucosa in their differential diagnosis, especially in atypical cases involving mucosal lesions.
"Early diagnosis can transform the treatment landscape for patients with melanoma mucosa, ultimately leading to better outcomes."
In summary, the diagnosis of melanoma mucosa requires a multi-faceted approach that includes clinical evaluation, imaging, biopsy, and consideration of differential diagnoses. These steps are crucial for ensuring accurate identification and prompting timely, appropriate intervention.
Pathophysiology of Melanoma Mucosa
The pathophysiology of melanoma mucosa is critical to comprehending how this rare form of melanoma develops and progresses. Understanding these mechanisms provides insights that can inform both diagnosis and treatment strategies. This section focuses specifically on genetic and molecular factors as well as the immune response, both of which play significant roles in the disease process.
Genetic and Molecular Factors
Mucosal melanoma often involves complex genetic alterations. Unlike cutaneous melanoma, which frequently displays mutations in the BRAF gene, mucosal melanoma may present with mutations in other genes such as KIT, NRAS, and more. These mutations can lead to uncontrolled cellular growth and malignancy.
- BRAF Mutations: While less frequent in mucosal melanoma, when present, BRAF mutations can influence therapy decisions.
- KIT Mutations: More often seen in mucosal sites, KIT mutations point to a specific pathway for targeted therapies.
- NRAS Mutations: These mutations might be present, affecting the signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation.


The epigenetic landscape also creates a crucial difference in mucosal melanoma. Factors like DNA methylation and histone modification can regulate gene expression, potentially leading to immune evasion. Thus, understanding these molecular dynamics is essential for developing effective therapeutic interventions.
"Genetic research on mucosal melanoma shows promise in identifying candidates for targeted therapies that may improve clinical outcomes."
Role of the Immune System
The immune system’s role in mucosal melanoma is remarkably complex and multifaceted. This type of melanoma often develops in areas where the immune response can be dampened or altered. Understanding how the immune system interacts with melanoma cells reveals vital strategies for intervention.
- Immune Evasion: Melanoma cells in mucosal regions may utilize mechanisms to evade detection. This can include upregulating checkpoint proteins, which inhibit T-cell activation.
- Microenvironment Influence: The tumor microenvironment can support immune suppression, allowing melanoma cells to thrive. Regulatory T-cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells often accumulate in tumor regions, further curbing an effective immune response.
- Immunotherapy Potential: Given the immune system's complexities, checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab and nivolumab have shown some efficacy in treating mucosal melanoma. Their role in modulating immune responses presents an ongoing area of research.
In summary, the pathophysiology of melanoma mucosa emphasizes the necessity of truly understanding the genetic and immune aspects of the disease. This understanding can both influence therapeutic approaches and provide a more refined understanding of patient care strategies.
Treatment Options for Melanoma Mucosa
Treatment strategies for melanoma mucosa are crucial in improving outcomes for patients with this rare form of cancer. Effective treatment must consider the unique characteristics of mucosal melanoma, such as its location, advanced stage at diagnosis, and aggressive nature. Patients often face limited treatment options available, making it essential for practitioners to stay informed about the latest developments and therapeutic approaches available.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical intervention remains a primary treatment modality for localized mucosal melanoma. Complete surgical excision aims to remove the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue to prevent recurrence. The effectiveness of this approach highly depends on early diagnosis, as patients diagnosed at a later stage may not be surgical candidates due to tumor spread.
Complexity arises with surgical interventions due to the anatomical constraints of mucosal areas, such as in the oral cavity, nasal passages, or genital regions. For instance, resections in sensitive areas may require reconstructive surgery afterward. The impact on surrounding tissues, function, and aesthetics must also be thoroughly considered.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy presents another component of treatment for melanoma mucosa, particularly in cases where surgical options are limited. This form of localized treatment uses high-energy rays to target cancer cells, aiming to reduce tumor size or eradicate residual cancer after surgery. It is often complementary to surgery, especially for patients with positive margins or lymph node involvement.
However, the use of radiation must consider the potential side effects. Mucosal tissues are more sensitive and may react adversely. Managing these side effects and balancing the therapeutic benefits poses challenges for oncologists.
Systemic Therapy Approaches
Systemic therapy approaches, such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy, can play an important role in treating melanoma mucosa, especially in advanced stages. Traditional chemotherapy may not be the first-line treatment due to the limited efficacy observed in mucosal types compared to cutaneous melanoma. Targeted therapy exhibits promise, focusing on specific cellular pathways involved in cancer growth.
For instance, vemurafenib targets BRAF mutations, which can occur in some mucosal melanoma cases. Understanding the genetic makeup of the tumor is vital for determining the appropriate systemic therapy. Recognition of the specific biomarkers present in patient's tumors enhances the likelihood of treatment success.
Immunotherapy Innovations
Immunotherapy has emerged as a groundbreaking option for melanoma mucosa, leading to significant advancements in treatment. Approaches such as checkpoint inhibitors aim to activate the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Treatments like pembrolizumab and nivolumab have shown effectiveness in advancing skin melanoma, sparking interest in their application to mucosal cases. However, clinical trials are still ongoing to better understand their efficacy and safety in this specific group.
Despite these advancements, not all patients will respond favorably to immunotherapy. The mechanisms behind these responses remain unclear and are a significant area of current research. Evaluating patient-specific factors, including tumor microenvironments and immune profiles, can help optimize treatment protocols.
Ongoing research efforts continue to explore combination therapies that integrate various treatment modalities for improved therapeutic outcomes.
Strengthening treatment options for melanoma mucosa involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual patient. As understanding increases, the diversification of available therapies, along with continued research, may significantly enhance prognosis and quality of life for patients facing this challenging disease.
Ongoing Research in Melanoma Mucosa
The realm of ongoing research in melanoma mucosa serves as a pivotal cornerstone in enhancing understanding and treatment methodologies for this rare disease. The complexity of mucosal melanoma necessitates continuous examination of its unique biological behaviors and responses to treatment. By focusing on specific advancements, researchers aim to improve early detection, optimize treatment protocols, and ultimately enhance patient prognosis.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are essential in assessing the safety and efficacy of new therapies for mucosal melanoma. These studies offer a structured framework for testing innovative treatment approaches, ranging from targeted therapies to combinations of standard treatments. In recent years, there has been a noticeable increase in the number of clinical trials focusing on mucosal melanoma. This surge is partly fueled by growing awareness of the condition and its distinctive characteristics compared to cutaneous melanoma.
Participation in clinical trials can provide patients with access to cutting-edge therapies that are not yet widely available. Moreover, these studies contribute valuable data to the medical community, aiming to refine treatment protocols. Some promising clinical trials investigate
- Checkpoint inhibitors, which may enhance the immune system's ability to fight cancer.
- Molecular targeted therapies, focusing on genetic mutations specific to mucosal melanoma.
- Combination therapies, which use multiple treatment modalities to achieve better outcomes.
As research evolves, it is vital that patients and healthcare professionals remain informed about ongoing and future clinical trials, ensuring that they consider all available therapeutic options.
Emerging Therapies
Emerging therapies represent another critical focus of ongoing research in the field of mucosal melanoma. Innovations in treatment are showing potential in delivering better results for patients. Some of the notable areas under investigation include:
- Novel immunotherapies: Exploring ways to harness the body's immune system to target and destroy melanoma cells more effectively.
- Targeted therapy advancements: New drugs that specifically inhibit pathways crucial for the growth of mucosal melanoma.
- Adjuvant therapies: Strategies that are explored alongside standard treatments to improve long-term outcomes for patients.


These emerging therapies not only aim to improve survival rates but also seek to minimize side effects and enhance the quality of life for patients. Given the aggressive nature of mucosal melanoma, research efforts are crucial in unraveling its complexities, thus providing hope for improved methodologies and results.
"Ongoing research into mucosal melanoma is essential not just for advancements in treatment but also for enriching the understanding of this complex disease."
As we navigate this intricate landscape, it becomes increasingly clear that continuous investment in research is key. The insights gained through trials and the introduction of emerging therapies not only illuminate potential pathways for effective treatment but also drive collective efforts towards discovering a cure.
Psychosocial Impact of Melanoma Mucosa
Mucosal melanoma is not only a medical concern; it also significantly affects the psychosocial dimensions of a patient's life. The diagnosis of melanoma mucosa often comes with challenges that impact mental health and social well-being. Patients and their families face a unique set of emotional and psychological challenges that necessitate a comprehensive understanding of these factors.
Mental Health Considerations
The mental health impact of melanoma mucosa can be profound. Patients frequently experience anxiety, depression, and distress related to the uncertainty of their prognosis and the severity of their condition. The rare nature of the disease can lead to feelings of isolation. Individuals may feel their concerns are not understood by others, thus intensifying their emotional burden. Research indicates a strong correlation between cancer diagnoses and mental health disorders, emphasizing the need for tailored psychological support.
Some studies suggest that mental health issues can adversely affect treatment outcomes. Patients struggling with depression may exhibit lower adherence to treatment regimens. This highlights the importance of integrating mental health screening and intervention in the care of patients diagnosed with melanoma mucosa. Effective support can help in managing these mental health challenges, fostering resilience, and potentially improving overall treatment efficacy. The role of support groups, therapy, and specialized care cannot be understated.
Support Systems and Resources
Support systems play a crucial role in coping with the psychosocial effects of melanoma mucosa. Family, friends, and healthcare providers can provide the emotional support that patients need during their journey. Open communication within these circles can help diminish feelings of isolation.
Various resources are available to individuals dealing with mucosal melanoma. Support groups, both online and in-person, can provide communities where patients share their experiences and coping strategies. These gatherings create a sense of belonging and understanding that is vital for emotional well-being.
In addition to peer support, psychological counseling can be beneficial. Professionals skilled in oncology care can offer significant assistance tailored to the unique challenges of mucosal melanoma.
Here are some valuable resources for patients and families:
- American Cancer Society – Provides comprehensive information about melanoma and offers support resources.
- National Cancer Institute – Offers information on clinical trials and treatment updates.
- Facebook Groups – Online communities can also be helpful for sharing personal stories.
"Support is vital. It can make all the difference in coping with the mental health impact of melanoma."
Future Directions in Research and Treatment
The exploration of future directions in the research and treatment of melanoma mucosa is critical for several reasons. Understanding the complexities associated with this rare type of melanoma opens up paths to better patient outcomes. As we delve into integrative approaches and global collaboration efforts, we see how these new trends could revolutionize how we approach this disease.
Integrative Approaches
Integrative approaches focus on combining conventional medical treatments with complementary therapies. Such strategies seek to enhance the overall effectiveness of treatment protocols for melanoma mucosa. Recent studies indicate that integrating emotional and psychological support can improve patient resilience. This approach includes:
- Psychotherapy: Helping individuals cope with the stress and emotional burden of diagnosis.
- Nutritional interventions: Exploring diets that support immune functions.
- Physical activity: Encouraging exercise that is appropriate for patients, which can enhance overall well-being.
The combination of these modalities addresses not just the cancer but the patient's holistic health. By treating the whole person, we can potentially improve quality of life during the treatment process.
Global Collaboration Efforts
Global collaboration is essential in advancing our knowledge and treatment of melanoma mucosa. Such efforts can facilitate:
- Shared knowledge: International experts can exchange information about treatment protocols and patient experiences.
- Diverse clinical trials: Collaborations can widen access to clinical trials, offering more patients the chance to receive cutting-edge therapies.
- Resource sharing: Institutions around the world can pool resources for research, lowering costs and increasing impact.
An example of this cooperation is initiatives like the Melanoma International Foundation. They promote networking among oncologists and researchers worldwide. By coming together, professionals can tackle the unique challenges posed by mucosal melanoma, including its delayed diagnosis and aggressive nature.
"Collaboration in research is not just beneficial; it is essential for advancing our understanding and treatment of rare cancers like melanoma mucosa."
End
The conclusion serves as a critical component of this article. It synthesizes the core insights gathered throughout the discussion about mucosal melanoma. Understanding this form of melanoma is paramount, particularly due to its rarity and aggressive nature. By summarizing key points, the conclusion emphasizes the multifaceted aspects of diagnosis, treatment, and emotional impact.
Furthermore, it offers a chance to reinforce the importance of awareness around mucosal melanoma. Patients and healthcare providers need to recognize the signs and symptoms early, as this can significantly affect outcomes. Enhancing public awareness about this type of cancer is essential for early detection and treatment. Public education can lead to improved patient outcomes, which is a major consideration in any discussion about cancer therapies.
Summary of Key Points
- Mucosal melanoma is rare and affects mucosal tissues.
- Early diagnosis is complicated due to nonspecific symptoms and locations.
- Characteristics include varied histological and morphological features.
- Treatment options range from surgical interventions to immunotherapy innovations.
- Ongoing research focuses on understanding genetic factors and developing emerging therapies.
- Psychosocial aspects must be considered to support patients effectively.
By summarizing these elements, we highlight the comprehensive nature of the disease and the need for continuous research and education.
Call to Action for Awareness
Raising awareness about mucosal melanoma is essential. Educational initiatives can empower patients and families to seek help when necessary. Organizations can play a pivotal role by providing resources and support to the community. Potential strategies include:
- Hosting informational sessions to educate healthcare professionals and the public.
- Collaborating with research institutions to fund studies on mucosal melanoma.
- Creating online platforms and support groups for families affected by this condition.
Such actions can facilitate better understandings among patients regarding their diagnosis and treatment options. The goal is to ensure that this rare but serious form of melanoma is recognized and treated as early as possible. This enhances not only survival rates but also the quality of life for those affected.



